QEMU调试Linux内核环境搭建
作者:快盘下载 人气:一个最小可运行Linux操作系统需要内核镜像bzImage和rootfs;本文整理了其制作、安装过程;调试命令;以及如何添加共享磁盘。
编译内核源码
从 The Linux Kernel Archives 网站下载内核源码;本文下载的版本为4.14.191;4.14.191源码下载。
使用wget获取源码。
wget https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v4.x/linux-4.14.191.tar.gz
解压源码;
tar -xvf linux-4.14.191.tar.gz
解压后进入源码根目录linux-4.14.191;指定编译的架构;依次执行下面的命令;打开配置菜单。
1cd linux-4.14.191 2 3export ARCH=x86 4 5make x86_64_defconfig 6 7make menuconfig
在配置菜单中;启用内核debug;关闭地址随机化;不然断点处无法停止。
1Kernel hacking ---> 2 [*] Kernel debugging 3 Compile-time checks and compiler options ---> 4 [*] Compile the kernel with debug info 5 [*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debuggin 6 7 8Processor type and features ----> 9 [] Randomize the address of the kernel image (KASLR)
开始编译内核;-j 指定并行编译作业数。最终生成
linux-4.14.191/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage文件。
1make -j 20
内核编译完成。
内核资料直通车;最新Linux内核源码资料文档;视频资料https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//docs.QQ.com/doc/DTmFTc29xUGDNSnZ2
内核学习直通车;Linux内核源码/内存调优/文件系统/进程管理/设备驱动/网络协议栈https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//ke.qq.com/course/4032547%3FflowToken%3D1040236
配置Busybox
启动内核还需要一个具有根文件系统的磁盘镜像文件;根文件系统中提供可供交互的shell程序以及一些常用工具命令。
我们借助busybox工具来制作根文件系统。
本文使用1.32.0版本;下载busybox。
解压;
tar -jxvf busybox-1.32.0.tar.bz2
进入busybox根目录;配置编译选项。
1cd busybox-1.32.0 2make menuconfig
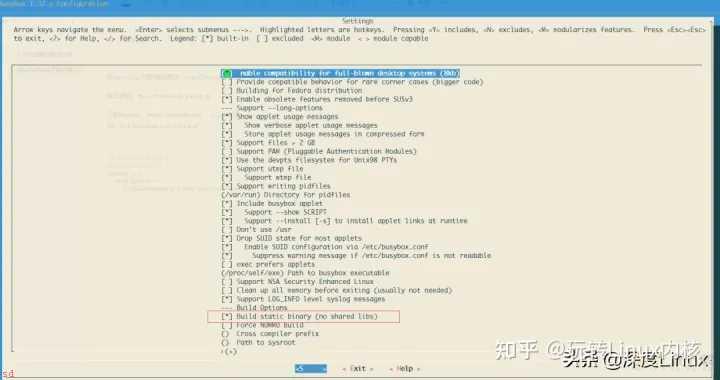
把busybox配置为静态编译。
1 Settings ---> 2 [*] Build BusyBox as a static binary (no shared libs)
配置如下图所示。
制作rootfs
接下来制作rootfs镜像文件;并把busybox安装到其中。
使用dd命令创建文件;并格式化为ext4文件系统。
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0$ dd if=/dev/zero of=rootfs.img bs=1M count=10 2 3szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0$ mkfs.ext4 rootfs.img
创建用于挂载该镜像文件的目录fs;挂载后才能往里面写入busybox。
使用mount命令将rootfs.img挂载到fs目录;编译busybox并写入fs目录中。
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~$ mkdir fs 2 3szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0$ sudo mount -t ext4 -o loop rootfs.img ./fs 4 5szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0$ sudo make install CONFIG_PREFIX=./fs
接下来对写入的busybox进行补充配置。
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0/fs$ sudo mkdir proc dev etc home mnt 2 3szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0/fs$ sudo cp -r ../examples/bootfloppy/etc/* etc/ 4 5szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0$ sudo chmod -R 777 fs/
制作完成的rootfs目录如下;

最后;卸载rootfs.img
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/busybox-1.32.0$ sudo umount fs
至此;一个带有rootfs的磁盘镜像制作完成。
启动qemu
使用如下命令启动无GUI的qemu;参数含义如下;
-kernel # 指定编译好的内核镜像
-hda # 指定硬盘
-append ;root=/dev/sda; 指示根文件系统 console=ttyS0 把QEMU的输入输出定向到当前终端上
-nographic 不使用图形输出窗口
-s 是-gdb tcp::1234缩写;监听1234端口;在GDB中可以通过target remote localhost:1234连接
1qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ./linux-4.14.191/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage -hda ./busybox-1.32.0/rootfs.img -append ;root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0; -nographic
启动后如下图;
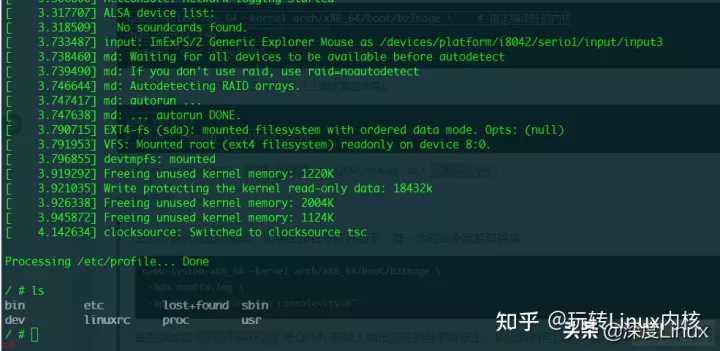
Ctrl;A 松开后按C退出qemu。
内核函数调试
启动命令中添加-s参数与-S参数启动qemu。
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~$ qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ~/linux-4.14.191/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage -hda ~/busybox-1.32.0/rootfs.img -append ;root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0; -s -S -smp 1 -nographic
启动gdb远程调试。vmlinux文件在编译后的内核源码根目录下。
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~$ gdb ./linux-4.14.191/vmlinux 2 3(gdb) target remote localhost:1234
在new_sync_read函数添加断点;continue。
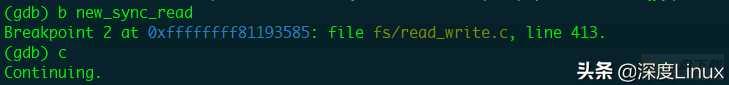
在系统中执行ls命令;触发new_sync_read函数;
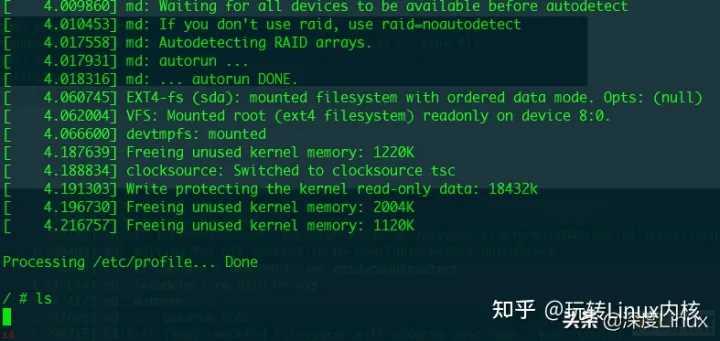
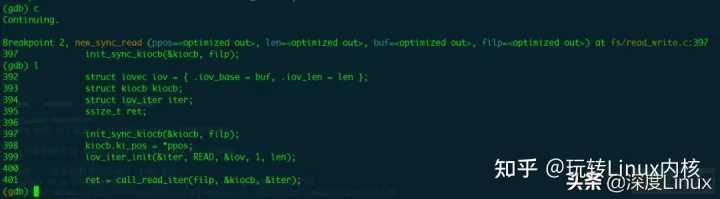
至此;完成了qemu环境下使用gdb进行内核函数的调试。
添加共享磁盘
有时候需要在宿主机和qemu虚拟机之间共享文件;添加一个共享磁盘将有助于该项工作。
创建64MB磁盘镜像文件;并格式化为ext4;作为共享磁盘备用。
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/shadisk$ dd if=/dev/zero of=ext4.img bs=512 count=131072 2 3szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/shadisk$ mkfs.ext4 ext4.img
修改qemu启动命令;使用-hdb增加一个磁盘。
1qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ~/linux-4.14.191/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage -hda ~/busybox-1.32.0/rootfs.img -append ;root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0; -s -smp 1 -nographic -hdb ~/shadisk/ext4.img
进入qemu系统后使用mount命令挂载sdb到mnt目录。
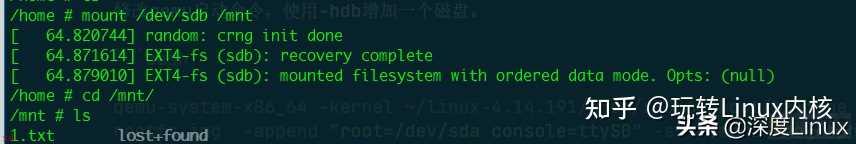
在原系统中挂载ext4.img;实现qemu与原系统的文件共享。
1szp;r420-PowerEdge-R420:~/shadisk$ sudo mount -t ext4 -o loop ext4.img ./share
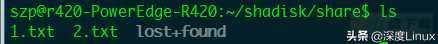
至此;可以在宿主机器share目录下;与qemu中的虚拟机器进行文件共享。
加载全部内容